How To Keep Estradiol Patch On Transgender
Feminizing Hormone Therapy
The goal of hormone therapy in trans women is to reduce the endogenous furnishings of testosterone such every bit coarse body hair and facial hair; and to induce female person secondary sex characteristics such every bit breast and hip evolution. Physiologically, this requires a suppression of endogenous androgens and the improver of estrogen.
Hormonal agents
Anti-androgens
Spironolactone has traditionally been used preferentially every bit it was thought to take a superior safe profile. This exercise has recently come up into question every bit it has been noted that adequate anti-androgen effects are achievable at lower doses of cyproterone at which adverse furnishings are less likely. Thus the choice of anti-androgen should be made individually for each client based on their medical history and preference regarding respective side issue profiles.
Following orchiectomy (+/- vaginoplasty), most trans women volition not require androgen suppression. The androgen-blocker can be tapered over the course of 4-6 weeks.
Estrogen
Estrogen acts directly on estrogen receptors to initiate feminization. It is unremarkably the focus of hormonal transition for trans women. The starting dose of estrogen tin be maintained for one-2 months, after which a dose increase tin be considered barring any apropos effects. In clients over 50 years old who have been on estrogen for several years, doses may be reduced to those administered to post-menopausal cis women (ie. 0.025 – 0.05 mg patch).
Expected effects
What to await from a regimen consisting of an anti-androgen and estrogen
The degree and rate of physical effects is dependent on the dose and road of administration, besides every bit client-specific factors such as historic period, genetics, body habitus and lifestyle.
Physical changes related to androgen occludent and estrogen may take months to announced and are generally considered to exist complete afterwards 2-iii years on hormone therapy. Feminizing therapy does not bear on the pitch of the vox in trans women. Some clients may obtain benefit from voice therapy with a qualified and supportive speech and language therapist who can work with the client to modify their song characteristics.
Effects and expected time course Download
Risk mitigation
Absolute contraindications
- Unstable ischemic cardiovascular illness
- Estrogen-dependent cancer
- End stage chronic liver disease
- Psychiatric weather condition which limit the ability to provide informed consent
- Hypersensitivity to one of the components of the formulation
Precautions and risk mitigation Download
Several pre-existing medical weather and risk factors may increase the risks associated with estrogen assistants. When these are present, a careful evaluation of risks and benefits should be completed and fully discussed with the client.
Precautions in cherry-red impart moderate to loftier risk of an adverse outcome without take chances mitigation.
Select area of concern beneath
Neurologic
More data on seizure disorders and anticonvulsant therapy on page 17 of the full Protocols
| Take a chance factors | How to minimize risks |
|---|---|
| Cerebrovascular affliction | Consider referral to neurology, ensure optimal medical management (including safety anticoagulation) and ambitious risk gene optimization, use transdermal route of assistants +/- lower dose |
| Severe refractory or focal migraine | Consider referral to neurology, consider daily migraine prophylaxis, ensure all other cerebrovascular take chances factors are optimized, consider transdermal route of administration |
| Seizure disorders | Consider referral to neurology, consult with a pharmacist re: impact of estrogen interaction with anticonvulsant medication |
| History of benign intracranial hypertension | Consider referral to neurology/neurosurgery |
Endocrine
| Risk factors | How to minimize risks |
|---|---|
| Hyperprolactinemia | Refer to endocrinology, defer initiation until etiology determined, manage based on etiology. More information on hyperprolactinemia/Prolacinoma on page 17 of the full Protocols |
| Marked hypertriglyceridemia | Identify and address barriers to optimal lipid control, refer to dietician, minimize alcohol consumption, consider anti-lipemic pharmacologic therapy, consider endocrinology referral, encourage deferral of estrogen until controlled, consider transdermal route of assistants |
| Uncontrolled diabetes | Identify and address barriers to optimal glycemic control, refer to dietician, encourage lifestyle modification, initiate antiglycemic agent(s), encourage deferral of estrogen until controlled, consider cardiac stress test, consider transdermal road of administration. |
| Metabolic syndrome | Dietary and medical direction of component disorders, encourage deferral until components adequately managed, consider cardiac stress examination, consider transdermal route of administration |
Cardiovascular
More information on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease on page 17 of the full Protocols
| Gamble factors | How to minimize risks |
|---|---|
| Stable ischemic cardiovascular disease | Consider referral to cardiology, ensure optimal medical (including prophylactic anticoagulation) and/or surgical management as indicated, aggressive chance gene optimization, use transdermal road of assistants +/- lower dose |
| Other cardiac diseases | Consider referral to cardiology |
| Uncontrolled high blood pressure | Place and address barriers to optimal BP command, use spironolactone as antiandrogen, add together additional antihypertensives as needed (avoid ACEs/ARBs with spironolactone), encourage deferral of estrogen until controlled, consider cardiac stress examination, consider transdermal road of administration |
Hepatic
More information on liver/gallbladder effects on page 17 of the full Protocols
| Risk factor | How to minimize risks |
|---|---|
| Hepatic dysfunction | Dependent on etiology, eg. minimize alcohol consumption, weight loss in NAFLD, consider referral to hepatology/GI, use transdermal or injectable route of assistants |
Oncologic
More than information on breast cancer on page 17 of the full Protocols
| Risk factors | How to minimize risks |
|---|---|
| Strong family history of breast cancer | Refer to genetics/familial chest cancer program for farther risk stratification and BRCA1/2 testing as indicated |
Hematologic
| Chance factors | How to minimize risks |
|---|---|
| Personal or family unit history of porphyria (rare) | Consider referral to porphyria clinic or internist with experience in porphyria |
| Personal history of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE) | Identify and minimize co-existent chance factors, consider prophylactic anti-coagulation, consider referral to hematology, use transdermal route of administration +/- lower dose |
| Family history of abnormal clotting | Consider referral to hematology, rule out genetic clotting disorder, consider condom anticoagulation, utilise transdermal route of assistants |
Respiratory
| Risk/Precaution | How to minimize risks |
|---|---|
| Smoker | Encourage and support smoking cessation, offer NRT and/or bupropion/varenacline, or negotiate a decrease in smoking, consider lower dose, consider cardiac stress test, use transdermal route of administration |
Monitoring strategies
Standard monitoring of estrogen administration should be employed at baseline, 1, 3, 6, and 12 months. This should include a functional inquiry, targeted physical exam, bloodwork, and wellness promotion/ illness prevention counselling.
Testosterone level may be the near useful test for monitoring in trans women; for many clients, the goal will be to achieve the suppression of testosterone into the female range. That said, the client may have clinically relevant results without total suppression of testosterone because of androgen blockade, which is not easily measured. Estradiol levels are of variable utility in monitoring feminizing therapy given the wide cyclical variation in cis women. Most clients reach considerable feminization at estradiol levels between 200-500 pmol/L. According to the Endocrine Society Guidelines, serum estradiol levels should not exceed the mean daily level for cis women (approximately 700 pmol/L).
Long-term preventive care
Trans women maintained on feminizing hormone therapy take unique preventive intendance needs and recommendations.
Long-term care of trans women on feminizing hormone therapy should involve (at least) annual preventive care visits. An Adaptive Preventive Care Checklist with accompanying explanations for trans-specific recommendations can be accessed beneath.
Preventive care screening procedures
Physical examinations that involve intimate body parts are discomforting to anyone. While many trans people are comfortable with their bodies others may feel body dysphoria. Some may be very uncomfortable with concrete examinations or be reluctant to acknowledge or touch on their own genitals.
Provide intendance based on organs present
It is best to base routine screening on the presence or absenteeism of body parts. Sex assigned at birth and gender identity are divide things. Some women have pensises, some men accept vaginas. Refrain from calling torso parts 'male' or female'. Instead use technical terms or enquire customer what they prefer to call their body parts. Organs nowadays should receive routine and preventive care.
Click on i of the tabs to find out routine care and screening suggestions.
Osteoporosis and Os Mineral Density Screening
Indications for BMD screening
- Clients over 65 years old
- Clients over 50 years quondam and with higher chance for osteoporosis
- Clients with any other risk factors for osteoporosis or bone loss (glucocorticoid therapy, previous fractures, family history of osteoporosis)
- Agonadal clients with eleveated LH levels
- Clients at whatever age having undergone orchiectomy and having been off exogenous hormones for any pregnant length of time
- Clients on anti-androgen therapy for a significant length of time without co-administration of exogenous estrogen
Chest exam
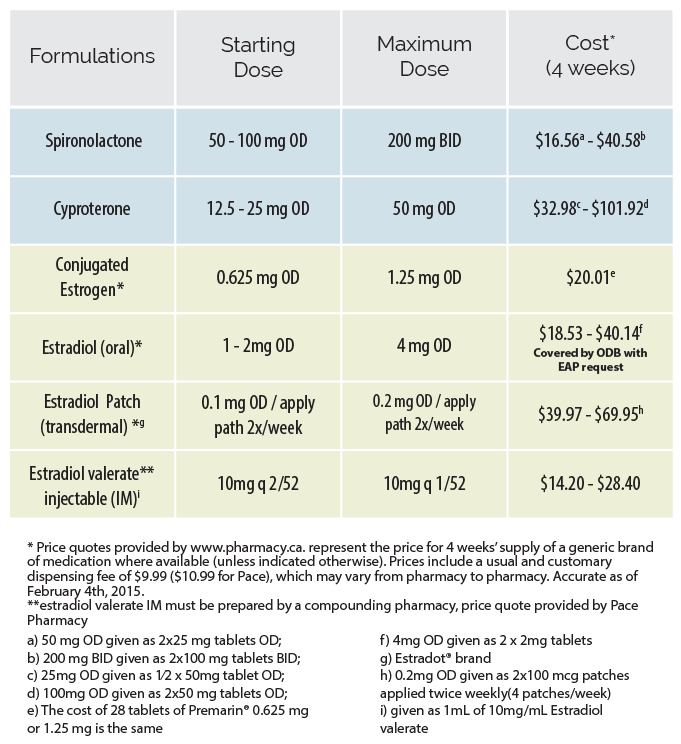
Employ the diagram below to discover out whether your client needs breast cancer screening.
Colon cancer screening
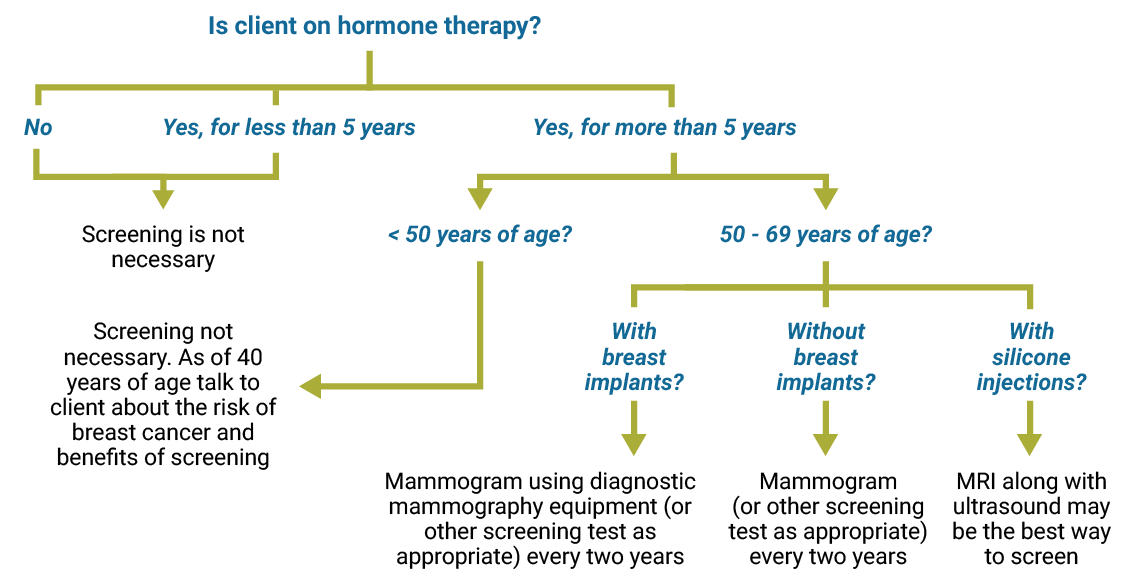
Utilise the diagram below to find out when and what type of colon cancer screening is recommended.
Cervical cancer screening
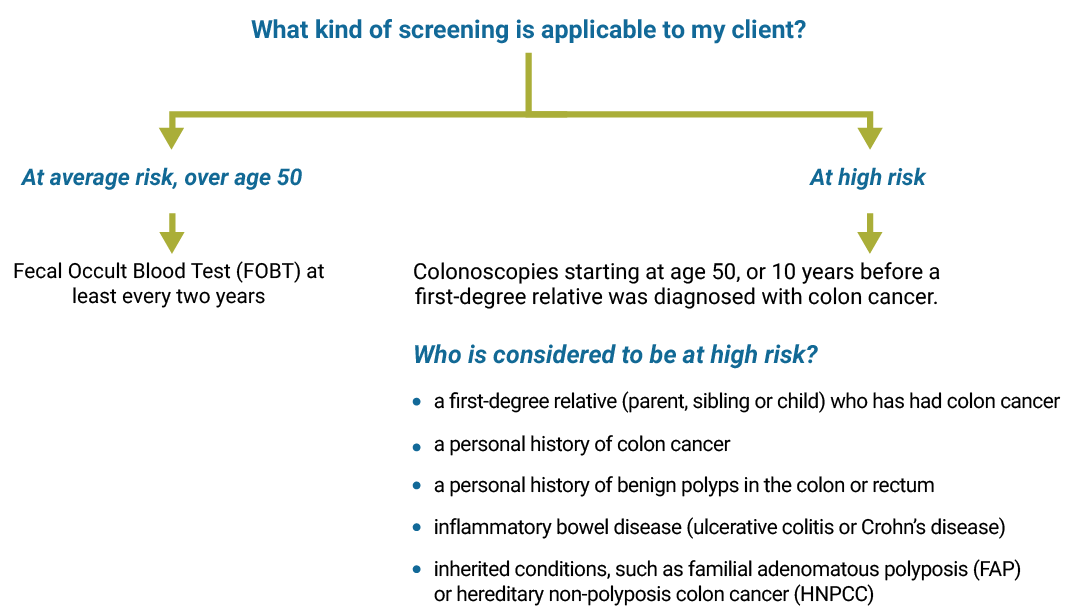
Utilise the diagram beneath to find out what type of cervical cancer screening is recommended.
Prostate exam
The risk of prostate cancer is not increased past estrogen use, in fact it is reasonable to assume that the risk is significantly decreased by the associated androgen impecuniousness. Although rare, there have been cases of prostate cancer reported in trans women, generally occurring in those who started hormone therapy after the age of l.1, two It is important to note that estrogen will lower PSA values fifty-fifty in the presence of prostate cancer, thus impacting its utility in this population. Routine PSA screening is non recommended in trans women in the absence of pregnant adventure factors. There is little testify to support a role for annual DRE in prostate cancer screening; still, it may be considered according to a provider's routine practice with cis men. In clients who have undergone vaginoplasty, the prostate remains in situ and may be palpated anteriorly via digital vaginal exam in a gender affirming lithotomy position.
Sources
- Gooren LJ, Giltay EJ, Bunck MC. Long term treatment of transsexuals with cross-sex hormones: extensive personal experience. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93(1):19-25.
- Mueller A, Gooren L. Hormone-related tumors in transsexuals receiving treatment with cross-sex hormones. Eur J Endocrinol. 2008; 159(3):197-202.
Copyright ©2016 Rainbow Wellness Ontario and Kelly Speck
Source: https://bmc1.utm.utoronto.ca/~kelly/transprimarycare/gp-femht.html
Posted by: charlesmistabou.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Keep Estradiol Patch On Transgender"
Post a Comment